What is Beta Testing?
Beta testing is the process after completion of alpha testing. Prototypes in beta testing are much closer to the final solution than alpha prototypes. Beta testing prototypes are not tested within the developer’s institute any more. Instead. They are usually tested by the prospective consumers as well as general public.
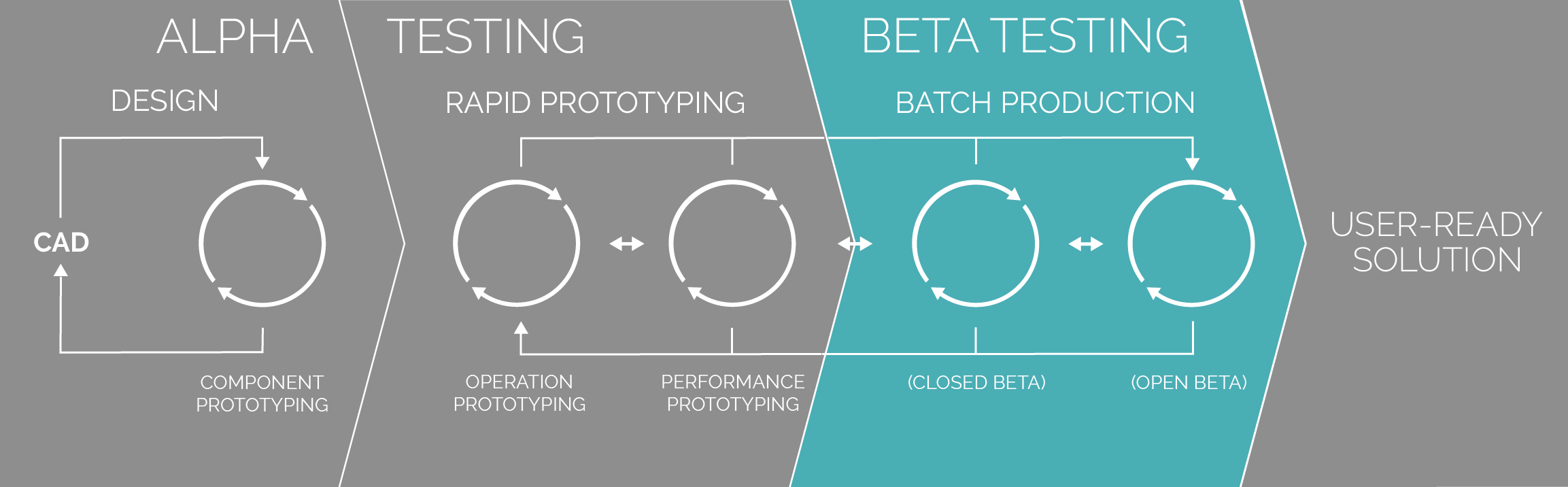

Closed Beta
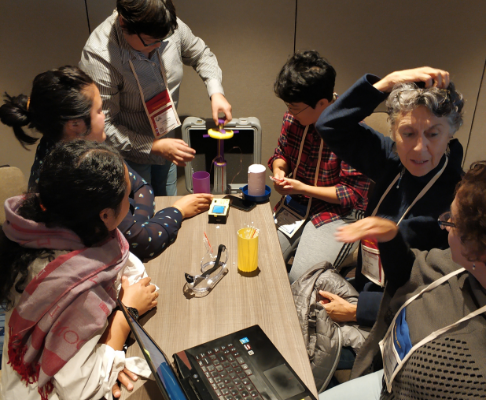

In 2019, the Cajun Ejector prototypes were evaluated in beta-testing event held during the World Aquaculture Society conference in New Orleans, USA. More than 50 international researchers, potential users, and federal and state staffs participated in the beta testing.
Prototypes in beta testing have all the functions in place that are expected for the final solutions. They have fewer flaws than the alpha prototypes. The documentation is almost complete or close to complete, and the prototypes are usually ready to perform or operate in the real-world environment.

Open Beta
Now, we should already have the prototypes in assemblies that are ready to be tested for performing their desired functions. At this stage, the prototypes are usually evaluated to see if they can achieve the desired design goals. Objective measurement are usually taken, such as cooling rate for freezing device, and accuracy and precision for measurement device. Data are analyzed and ‘refinement’ design change are made to fulfill envisioned functionalities.

Beta testing is usually shorter than alpha testing. The reason for this is that the beta testing
is usually designed to identify the minute, last-minute issues before the envisioned solution is
launched in the public users.
There are two major steps of beta testing. In the closed beta testing, potential users with
considerable experience and expertise in the relevant field participated in the evaluation. The
open beta testing would involve general public who may never have any experience in using the
prototypes or previously knowledge in the field.